Checklist for Writing the Perfect College Paper
Checklist for Writing the Perfect College Paper
Professors may assume that students understand the basics when it comes to writing college research papers. In reality, many students are frustrated by all of the requirements. There are not a lot of easy checklists that put all of the requirements into one location. The following checklist should be used as a helpful guide to help college students write a well-researched and properly presented paper.
Write in introduction/body/conclusion format
- Introduction – The first paragraph introduces what will be included in the paper. It is a good idea to have the first sentence of the first paragraph include a hook to interest the reader. Students should list a few sentences that summarize the main topics that will be addressed in the paper. In this example, assume that three things will be covered based on the assignment requirements. End the introductory paragraph with the thesis statement.
- Body – The body is where the three things, required for the assignment, are addressed. Students should start each paragraph with a topic sentence. Students should write a few sentences about that topic. Students should end that paragraph with a transitional sentence that leads into the next topic that will be addressed in the following paragraph. This process should be completed for all paragraphs until the last paragraph.
- Conclusion – The last paragraph may begin with something like, “In conclusion”. This last paragraph will sum up the three topics addressed. The last sentence should restate the thesis statement listed in the introduction, and end with some sort of final prediction or conclusion.
Write in complete paragraphs – Paragraphs should ideally contain between 4-8 sentences. Students often make the mistake of writing in incomplete paragraphs or overly long paragraphs. Click here for more information about paragraph structure.
Avoid run-on sentences – Sentences should not be overly complex. Students should check how many times the word “and” is used. This may signal a run-on sentence.
Write in APA format – Set up papers that include a title page, double-spacing, indented paragraphs, page numbers, correctly cited sources, etc. per APA.
- Click here for an example of an APA paper.
- Click here for more help with APA.
- Click here for a site that makes citing easy.
- Click here for example papers, research and documentation help
Research the paper through the school’s library – Students often make the mistake of researching through the use of Google or other popular search engines. Students may also make the mistake of relying on sources that are less than scholarly. Sites like Wikipedia may offer some good information but they are not considered reliable or scholarly sources for research papers. Students should use the school’s search engine, located in the online library. Students should click the box that searches for scholarly, peer-reviewed journals to ensure the sources are appropriate.
Cite consistently and correctly throughout the paper – Students often make the mistake of thinking they are story-telling when they should be demonstrating research. Students should get into the habit of paraphrasing rather than listing direct quotations. Students should avoid patchworking. Students should not make the mistake of listing references without citations. This is a common mistake. Research papers require both citations AND references. Students should also not make the mistake of simply ending a paraphrased paragraph with (author last name, year) to cite all information covered in the paragraph. This is also a common mistake and can be considered plagiarism. Every sentence of paraphrased work requires the author and year information. Click here for information about how to cite.
Submit the paper to TurnItIn – Many schools offer TurnItIn’s plagiarism checker. This is an excellent tool that is helpful to both the students and the schools. Students should get in the habit of submitting his or her papers through this software program to insure that they are not inadvertently plagiarizing information.
Check narrative mode – Many courses do not allow students to write in first person. If this is the case, students should not refer to themselves. Students should look for words like I, we, us, me. These words should not be included if the paper does not allow first person.
Check Word document format – Students often overlook the settings in the Word document. Students should be sure that the font, margins and settings are correctly set to APA requirements.
- Click here for help with removing extra spaces between paragraphs.
- Click here for help with page numbers and headers.
- Click here for an example of an APA paper.
Check spelling and other miscellaneous issues – Students should read the final draft more than once. Even if everything seemed OK in the paper, it is a good idea, for students to read it several times to look for small errors. Students should check for spacing issues. Students should also check that there are two spaces after periods per APA. Students should spell-check the document to be sure all spelling issues are resolved.
Related Articles
- How to Write the Perfect College Paper: Video Tutorial
- Top 10 Most Common Writing Mistakes
- Top 100 Vocabulary Words That Adults Should Know
- Top 10 Tips for Surviving a Doctoral Dissertation
- Top 10 Sources for Help with APA 6th Edition
- New Studies Show Technology to Blame for Increase in Plagiarism
- How to Paraphrase and Avoid Using Direct Quotes
- How to Receive an A in Your College Courses
Credit Score Savvy
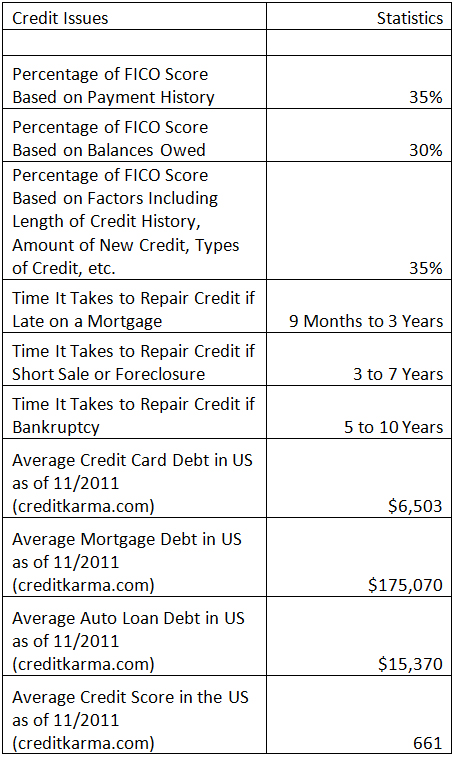
With the New Year, people often make resolutions to fix problem financial situations. Part of cleaning an individual’s financial house includes taking a hard look at his or her credit. Credit Score Savvy (2003) was one of my earlier articles that I wrote for a local magazine. At that time, I was a loan officer and found that many people were confused by FICO scores and credit issues. In the article I explained factors that affected scores and the ability to finance a home. Although the market has changed since then, a lot has remained the same in terms of confusion about credit issues. A more recent article titled Polish up Your Credit includes some information about things people can do to improve his or her credit score now. What may be most useful from this article are some of the statistics. The following chart provides answers to some of the most basic credit-related questions.
Related Articles
Doctoral Dissertation: Proposal Approval Checklist
In the years I have spent as a doctoral chair, I have read many excellent proposals and final dissertations. Writing a dissertation takes a great deal of patience and time. Some students may become frustrated if he or she believes that the process takes longer than anticipated. To avoid a lengthy proposal approval process, the student should spend time going over some common mistakes. Although each school may have different requirements, the following checklist may be helpful to the doctoral learner prior to submitting his or her proposal for review.
| Common Errors | Place X to Signify Compliance |
| All Required Forms Are Included | |
| Note That Data Will Be Saved 3 Years Then Destroyed | |
| Paragraphs Must Contain At Least 3 Sentences | |
| Any Defined Words Must Include A Citation | |
| 85% Of References Must Be Less Than 5 Years From Proposal Date | |
| All Sections Are Listed In Proposal | |
| References Are In APA Format | |
| Submit to TurnItIn Or Plagiarism Checker | |
| Submit To Editing Software Or Editor | |
| Submit To Statistician If Necessary | |
| Two Spaces Are Required After Periods | |
| Design Is Carefully Described | |
| Clarity – Person Reading Proposal Could Perform Study If Necessary | |
| No Personal Opinions – All Conclusions Substantiated | |
| The Word “Proposed” Is Listed Before Referring To Proposed Study | |
| No Use Of The Wording “The Researcher” To Refer To Writer Of Proposal | |
| No First Person References | |
| No Fluff Words Including: However, In Addition, Therefore, Etc. | |
| Proposal In Future Tense; Will Change To Past Tense After Study | |
| What Others Have Written In Past Tense | |
| Long Tables Should Be In Appendix | |
| Long Citations Cannot Be On Two Separate Pages – Must Be On One | |
| No Slang Is Included | |
| Use Words “Which and That” Correctly | |
| There Should Not Be Any Tracking Changes Left In Document | |
| Headings Must Be In APA 6th Format | |
| Chapter 1 Must Start On Page 1 | |
| Proposal Author’s Name Must Be Listed And Current Month/Year | |
| Watch Use Of The Word Randomly (Be Specific) | |
| No Anthropomorphisms Should Be Used | |
| Watch Implying Causal Relationship If None Exists | |
| Do Not Make Predictions | |
| Multiple Studies In Parentheses Require Names In Alphabetical Order | |
| Avoid Vague Statements Like Something Was “Poor” | |
| Articulate How Participants Were Selected | |
| Articulate What Was Done To Reduce Researcher Bias | |
| Do Not Use Vague Terminology Like “Others” | |
| United States Is U.S. And Not US | |
| 1980s Should Be 1980s And Not 1980’s | |
| Stick To One Subject Per Paragraph | |
| Do Not Write In Contractions (Do Not Is Correct – Don’t Is Not) | |
| Do Not Have Back to Back Charts With No Explanation | |
| Use He or She Rather Than They To Define Subject | |
| Be Sure All Chapters Include A Summary | |
| Target Population And Sample Is Clearly Described | |
| Hypotheses May Be Numbered And Supported By Narrative | |
| Choice Of Method Is Clear And Substantive | |
| Punctuation Should Be Inside Of Quotation Marks | |
| Collaborative Institutional Training Initiative (CITI) Is Completed | |
| Checklist Should Be Provided To Doctoral Chair | |
| Application Should State If Exempt and Why |
Related Articles
- How to Write a Perfect College Paper: Video Tutorial
- Top 10 Most Common Writing Mistakes
- Top 100 Vocabulary Words That Adults Should Know
- Top 10 Tips for Surviving a Doctoral Dissertation
- Top 10 Sources for Help with APA 6th Edition
- New Studies Show Technology to Blame for Increase in Plagiarism
- How to Paraphrase and Avoid Using Direct Quotes
- How to Receive an A in Your College Courses
- Sample Size Calculator
Top Links Explaining Texting (SMS) and Short Codes
Just as Twitter has grown to be an important marketing tool, texting is not just for stating LOL anymore. There are some very important uses for texting, aka SMS (short messaging service). Check out some helpful links to explain texting terminology and uses:
- Donate to Charity – Pew Research recently reported that almost 1 in 10 Americans donate to charity through texting.
- Search Sites Like Google – By texting GOOGL (46645), you can search Google without opening your browser. Check out: Six Things You Never Knew Your Cell Phone Could Do. Word/number texts like GOOGL (46645) are called common short codes. Check out: Basics of CSCs to find out everything you need to know about common short codes.
- Send and Receive Email – To find out how to use SMS to access email, check out: 16 Things You Can Do With SMS Text Messages.
- Check the Weather – By texting 4CAST (42278), you can access weather forecasts. Check out: Five Great Things You Can Do With a Text Message For Free.
- Check Calendar – By texting GEVENT (48368), you can access your Google calendar and schedule appointments. Check out: Ten Terrific Things You Can Do With Text Messaging.
- Track Packages – Your SMS can track your UPS, Fed Ex, DHL and other packages through TrackThis. Check out: Run Your Life with SMS: 10 Things You Didn’t Know You Could Do Via Text.
- Learn Texting Abbreviations – You may know LOL, but there is an entire site of information dedicated to explaining what all of those text messaging and online chat abbreviations mean and text message abbreviations.
- Text From a Computer – If you have a computer and someone’s 10-digit phone number, you can text them without needing a phone. The following explains how to text people based on their carrier (i.e., Verizon, AT&T, etc.): Text from a Computer.
- Create a Common Short Code (CSC) – You can create your own CSC campaign by leasing a code. Check out: Obtaining a CSC. Remember the CSC is like GOOGL or 4CAST noted above. Keep in mind that leasing the code is the first step. You’ll still need to negotiate agreements with each of the wireless carriers to activate your short code. To be part of the CSCA directory listing, click here.
- Enhance Business – Business can utilize short codes for contests, lead capture and more. Check out: Top 10 Business Goals Enhanced by Short Codes.
Related Articles
- Can Texting Damage Writing Skills?
- Use QR Codes to Promote Your Business
- Marketers Target Impatient Customers through Smartphone Quick Response QR Codes
- QR Code: Why You Should Be Using it to Promote You, Your Business and Products
- Is Email on Its Way Out?
- How Google Voice Works
- How Americans Use Text Messaging (Pew Research)
Importance of Being Proactive vs. Reactive
Many good foresight or business courses teach students to be proactive vs. reactive to change. Anyone who has read The 7 Habits of Highly Successful People will tell you that the very first habit Covey lists is to be proactive. Covey explained that to be proactive “means more than merely taking initiative. It means that as human beings, we are responsible for our own lives. Our behavior is a function of our decisions, not our conditions.”
When a person is in control of an expected or anticipated occurrence, they have taken proactive measures. When a person is reactive, they are responding to something that they had yet to have anticipated.
In leadership courses, they often give examples of a proactive vs. a reactive leader. The following chart gives an example of the different mindset of these two styles of leaders. Click on the picture for more information.
Carol Shultz’s article Proactive vs. Reactive Approaches to Your Business and Talent explained two cases that demonstrated how reactive companies lost employees for different reasons, and the associated costs.
There are a number of theoretical models for change that include the importance of being proactive. Some of these include:
- Lewin’s Three-Step Model for Change
- Bullock and Batten’s Phases of Planned Change
- Kotter’s Eight Steps
- Beckhard and Harris’s Change Formula
- Nadler and Tussman’s Congruence Model
- William Bridge’s Managing the Transition
- Carnall’s Change Management Model
- Senge’s Systemic Model
To read more about these and other models for change, click here.
Related Articles
- Top 25 Links to Change Your Body, Career and More
- Ten Entrepreneurs Who Hit It Big Before Turning 35
- Top 10 Companies Code of Ethics and Conduct
- Top 10 Company Mission Statements in 2011
- Famous Entrepreneurs Who Hit it Big With Humble Beginnings
- Researching Apple: Top 10 Most Useful Links
- Value of Top Companies in 2011
- The Top 10 Most Misunderstood Entrepreneurial Terms
- Top Five Things to Know to be a Successful Entrepreneur
- 50 Famous People Who Failed Before They Became Successful
- Top 50 Venture Funded Companies for 2011
- Top 5 Networking Tips for Small Businesses
- Time for a New Career? Change the Daily Grind to a Job of Your Dreams
- 50 Excellent Lectures for the Small Business Owner
- An Entrepreneur’s Startup Business Model Checklist